
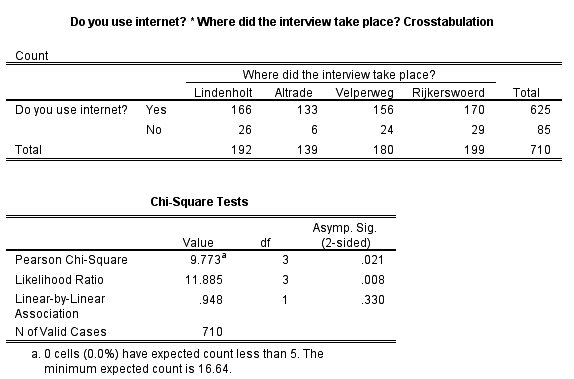
For each cell of the table, we have to calculate the expected value under null hypothesis. That means the row and column variables are dependent. Alternative hypothesis (H1): There is an association between the two variables.That means the row and the column variables of the contingency table are independent. Null hypothesis (H0): There is no association between the two variables.This calculated Chi-square statistic is compared to the critical value (obtained from statistical tables) with a degrees of freedom df = (r−1) × (c−1) and p = 0.05. Where, ‘r ‘is the number of rows and ‘c’ is the number of column in the contingency table.Ĭhi-square test examines whether rows and columns of a contingency table are statistically significantly associated. General notation for a 2 x 2 contingency table.įor a 2 x 2 contingency table the Chi Square statistic is calculated by the formula: If we set the 2 x 2 table to the general notation, using the letters a, b, c, and d to denote the contents of the cells, then we would have the following table: We’ll begin with the simplest case: a 2 x 2 contingency table. There are several types of chi square tests depending on the way the data was collected and the hypothesis being tested. contingency table) formed by two categorical variables. The chi-square test of independence is used to analyze the frequency table (i.e. The chi-square test is applied when you have two categorical variables from a single population and it evaluates whether there is a significant association between the categories of the two variables. When used for bivariate analysis – the analysis of two variables in conjunction with one another – it is called the chi-square test of association, or the chi-square test of independence, and sometimes the chi-square test of homogeneity.

Goodness of fit is used to determine whether sample data are consistent with a hypothesized distribution. In its univariate form –the analysis of a single variable – it is associated with the ‘goodness of fit’. Briefly, chi-square tests provide a means of determining whether a set of observed frequencies deviate significantly from a set of expected frequencies.Ĭhi-square can be used at both univariate and bivariate levels. The tests associated with this particular statistic are used when your variables are at the nominal and ordinal levels of measurement – that is, when your data is categorical.
#Chisquare in spss windows
Using SPSS for Windows and Macintosh: Analyzing and understanding data (7th ed.). There is a relationship between race and feelings about the bible. The results of the test were significant, x2 (6, N = 706) = 40.45, p <. The null hypothesis is: there is no relationship between race and feelings about the bible. The research question is: is there a relationship between race and feelings about the bible. The independent variable is race and the dependent variable is feelings about the bible. In addition, when the sample size is relatively large, the one-sample chi-square will produce a resulting statistic that is approximately distributed as a chi-square (Green & Salkind, 2014).Ī one-sample chi-square test was conducted to assess whether race has an effect on feelings about the bible. The statistical assumptions underlying the one-sample chi-square test are that the observations made must be from a random sample, and results from the observation are independent of each other (Green & Salkind, 2014). In addition, the statistical results of the chi-square will be analyzed. The purpose of this paper is to state the statistical assumptions of the chi-square, choose dependent and independent variables, develop the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis, use SPSS to calculate a chi-square, and decide whether to reject or retain the null hypothesis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
